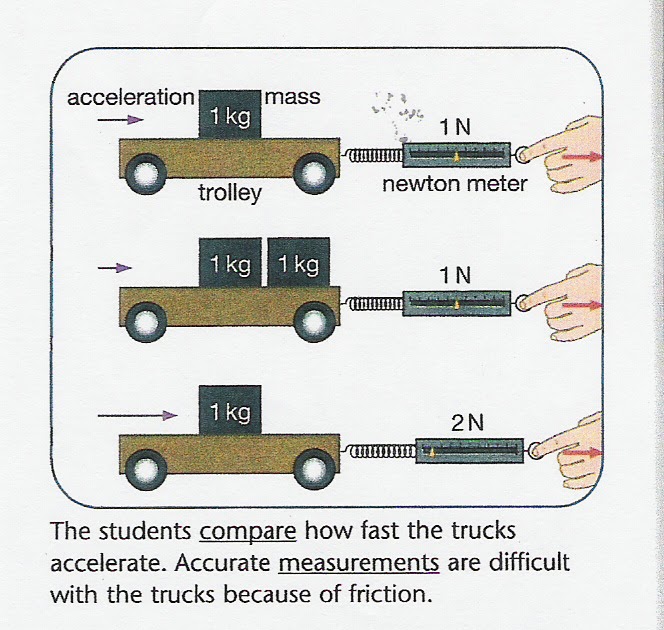
Lab 5 Force Mass And Acceleration . Appendix c objective the objective of this lab is to explore and analyze the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration. Behind newton’s second law is the assumption that an object (or group of objects) can be. A change in velocity means, by definition, that there is. Newton’s second law of motion gives a relationship among acceleration, force, and mass. You can conduct these two experiments using a. • to develop a definition of mass in terms of an object's acceleration under the influence of a force. The answer is that a change in motion is equivalent to a change in velocity. Accelerating a fixed mass with a variable force. It can help us make predictions. Theory according to newton’s second. Each of those physical quantities can be defined independently,. Applying the same force to an object of different mass affects the acceleration of the object. A soccer player kicks a 0.45 kg soccer ball,.
from roman-rodrigues.blogspot.com
It can help us make predictions. Appendix c objective the objective of this lab is to explore and analyze the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration. Applying the same force to an object of different mass affects the acceleration of the object. Each of those physical quantities can be defined independently,. You can conduct these two experiments using a. • to develop a definition of mass in terms of an object's acceleration under the influence of a force. Accelerating a fixed mass with a variable force. Theory according to newton’s second. A change in velocity means, by definition, that there is. A soccer player kicks a 0.45 kg soccer ball,.
EXPLORING Force, mass and acceleration
Lab 5 Force Mass And Acceleration Appendix c objective the objective of this lab is to explore and analyze the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration. Theory according to newton’s second. Applying the same force to an object of different mass affects the acceleration of the object. A change in velocity means, by definition, that there is. The answer is that a change in motion is equivalent to a change in velocity. Behind newton’s second law is the assumption that an object (or group of objects) can be. • to develop a definition of mass in terms of an object's acceleration under the influence of a force. Newton’s second law of motion gives a relationship among acceleration, force, and mass. It can help us make predictions. A soccer player kicks a 0.45 kg soccer ball,. Each of those physical quantities can be defined independently,. You can conduct these two experiments using a. Accelerating a fixed mass with a variable force. Appendix c objective the objective of this lab is to explore and analyze the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration.
From www.thesciencehive.co.uk
Forces (GCSE) — the science hive Lab 5 Force Mass And Acceleration You can conduct these two experiments using a. Theory according to newton’s second. The answer is that a change in motion is equivalent to a change in velocity. A change in velocity means, by definition, that there is. A soccer player kicks a 0.45 kg soccer ball,. Behind newton’s second law is the assumption that an object (or group of. Lab 5 Force Mass And Acceleration.
From owlcation.com
What Is a Force? Mass, Velocity, Acceleration and Adding Vectors Lab 5 Force Mass And Acceleration A soccer player kicks a 0.45 kg soccer ball,. • to develop a definition of mass in terms of an object's acceleration under the influence of a force. The answer is that a change in motion is equivalent to a change in velocity. Each of those physical quantities can be defined independently,. Accelerating a fixed mass with a variable force.. Lab 5 Force Mass And Acceleration.
From www.studocu.com
Lab 5 Force Mass and Acceleration PHYS 121 UMBC Studocu Lab 5 Force Mass And Acceleration The answer is that a change in motion is equivalent to a change in velocity. Behind newton’s second law is the assumption that an object (or group of objects) can be. Each of those physical quantities can be defined independently,. A change in velocity means, by definition, that there is. Newton’s second law of motion gives a relationship among acceleration,. Lab 5 Force Mass And Acceleration.
From www.scribd.com
Solving Problems Involving Resultant Force, Mass and Acceleration of An Lab 5 Force Mass And Acceleration A change in velocity means, by definition, that there is. You can conduct these two experiments using a. • to develop a definition of mass in terms of an object's acceleration under the influence of a force. Theory according to newton’s second. Appendix c objective the objective of this lab is to explore and analyze the relationship between force, mass,. Lab 5 Force Mass And Acceleration.
From www.mrcorfe.com
Force, Mass and Acceleration Lab 5 Force Mass And Acceleration You can conduct these two experiments using a. • to develop a definition of mass in terms of an object's acceleration under the influence of a force. Newton’s second law of motion gives a relationship among acceleration, force, and mass. Each of those physical quantities can be defined independently,. It can help us make predictions. Behind newton’s second law is. Lab 5 Force Mass And Acceleration.
From www.chegg.com
PRELAB PREPARATION SHEET FOR LAB 5 FORCE, MASs, AND Lab 5 Force Mass And Acceleration It can help us make predictions. The answer is that a change in motion is equivalent to a change in velocity. Applying the same force to an object of different mass affects the acceleration of the object. • to develop a definition of mass in terms of an object's acceleration under the influence of a force. You can conduct these. Lab 5 Force Mass And Acceleration.
From www.chegg.com
Solved HoMEWORK FOR LAB 5 FORCE, MASS, AND ACCELERATION . Lab 5 Force Mass And Acceleration Behind newton’s second law is the assumption that an object (or group of objects) can be. Applying the same force to an object of different mass affects the acceleration of the object. The answer is that a change in motion is equivalent to a change in velocity. A change in velocity means, by definition, that there is. Theory according to. Lab 5 Force Mass And Acceleration.
From studylib.net
Virtual Lab Force = Mass x Acceleration Lab 5 Force Mass And Acceleration Theory according to newton’s second. Accelerating a fixed mass with a variable force. Behind newton’s second law is the assumption that an object (or group of objects) can be. Applying the same force to an object of different mass affects the acceleration of the object. • to develop a definition of mass in terms of an object's acceleration under the. Lab 5 Force Mass And Acceleration.
From studylib.net
Experiment To show that the acceleration of a body is proportional Lab 5 Force Mass And Acceleration Accelerating a fixed mass with a variable force. A soccer player kicks a 0.45 kg soccer ball,. You can conduct these two experiments using a. Behind newton’s second law is the assumption that an object (or group of objects) can be. A change in velocity means, by definition, that there is. Appendix c objective the objective of this lab is. Lab 5 Force Mass And Acceleration.
From roman-rodrigues.blogspot.com
EXPLORING Force, mass and acceleration Lab 5 Force Mass And Acceleration Appendix c objective the objective of this lab is to explore and analyze the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration. Applying the same force to an object of different mass affects the acceleration of the object. The answer is that a change in motion is equivalent to a change in velocity. • to develop a definition of mass in terms. Lab 5 Force Mass And Acceleration.
From www.thinkswap.com
SPM Physics Experiment Force, Mass and Acceleration Physics Form 5 Lab 5 Force Mass And Acceleration Applying the same force to an object of different mass affects the acceleration of the object. The answer is that a change in motion is equivalent to a change in velocity. Accelerating a fixed mass with a variable force. Each of those physical quantities can be defined independently,. Behind newton’s second law is the assumption that an object (or group. Lab 5 Force Mass And Acceleration.
From www.chegg.com
Solved Name PRELAB PREPARATION SHEET FOR LAB 5 FORCE, Lab 5 Force Mass And Acceleration A change in velocity means, by definition, that there is. You can conduct these two experiments using a. It can help us make predictions. Each of those physical quantities can be defined independently,. Theory according to newton’s second. Behind newton’s second law is the assumption that an object (or group of objects) can be. The answer is that a change. Lab 5 Force Mass And Acceleration.
From www.youtube.com
F=ma Force is equal to mass times acceleration (Simple Problems Lab 5 Force Mass And Acceleration Accelerating a fixed mass with a variable force. The answer is that a change in motion is equivalent to a change in velocity. A change in velocity means, by definition, that there is. Newton’s second law of motion gives a relationship among acceleration, force, and mass. Theory according to newton’s second. Each of those physical quantities can be defined independently,.. Lab 5 Force Mass And Acceleration.
From wordwall.net
Mechanics Forces Demonstrate the relationship between mass and Lab 5 Force Mass And Acceleration Newton’s second law of motion gives a relationship among acceleration, force, and mass. It can help us make predictions. • to develop a definition of mass in terms of an object's acceleration under the influence of a force. Accelerating a fixed mass with a variable force. Applying the same force to an object of different mass affects the acceleration of. Lab 5 Force Mass And Acceleration.
From physicscalculations.com
How to Find Acceleration with Mass and Force Lab 5 Force Mass And Acceleration • to develop a definition of mass in terms of an object's acceleration under the influence of a force. You can conduct these two experiments using a. Theory according to newton’s second. Applying the same force to an object of different mass affects the acceleration of the object. Appendix c objective the objective of this lab is to explore and. Lab 5 Force Mass And Acceleration.
From www.studocu.com
Force Mass and Acceleration Lab Force, Mass, and Acceleration Name Lab 5 Force Mass And Acceleration A change in velocity means, by definition, that there is. Each of those physical quantities can be defined independently,. It can help us make predictions. Theory according to newton’s second. Appendix c objective the objective of this lab is to explore and analyze the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration. Applying the same force to an object of different mass. Lab 5 Force Mass And Acceleration.
From www.docsity.com
Force, Mass, and Acceleration Practice Problems Summaries Physics Lab 5 Force Mass And Acceleration Theory according to newton’s second. Behind newton’s second law is the assumption that an object (or group of objects) can be. Appendix c objective the objective of this lab is to explore and analyze the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration. Applying the same force to an object of different mass affects the acceleration of the object. The answer is. Lab 5 Force Mass And Acceleration.
From owlcation.com
Force, Mass, Acceleration and How to Understand Newton's Laws of Motion Lab 5 Force Mass And Acceleration It can help us make predictions. The answer is that a change in motion is equivalent to a change in velocity. A soccer player kicks a 0.45 kg soccer ball,. Newton’s second law of motion gives a relationship among acceleration, force, and mass. Theory according to newton’s second. Behind newton’s second law is the assumption that an object (or group. Lab 5 Force Mass And Acceleration.